Have you ever found yourself staring at a jumble of belts, pulleys, and hoses under the hood of your 2010 Ford Focus 2.0, feeling lost and overwhelmed? The thought of tackling a simple belt replacement can be daunting, especially without a clear understanding of how everything fits together. Fear not, for we’re about to demystify the intricate network of belts powering your car engine – the 2010 Ford Focus 2.0 belt diagram.
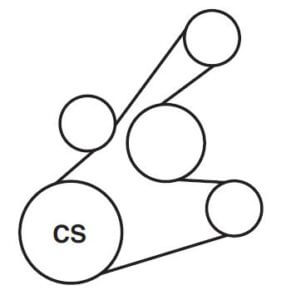
Image: beltposter.blogspot.com
This guide is your ultimate resource for navigating the complex world of engine belts. We’ll break down the diagram, explaining each component and its role, and providing expert advice to help you confidently tackle any belt-related tasks. From identifying the serpentine belt to understanding the tensioner system, we’ll ensure you’re equipped to keep your Focus running smoothly.
Understanding the 2010 Ford Focus 2.0 Belt Diagram
The Engine’s Lifeline: A Closer Look at the Belts
Imagine the engine as a bustling factory, with various machinery requiring power to function. The belts act as the power supply, transmitting energy from the crankshaft, the engine’s core, to auxiliary components like the alternator, water pump, and power steering pump.
The 2010 Ford Focus 2.0 typically utilizes a serpentine belt system, a single, continuous belt that loops around multiple pulleys. This setup simplifies maintenance as it reduces the number of individual belts needed. Understanding the belt diagram involves identifying the different pulleys and components each belt drives.
Decoding the Diagram and Understanding the Components
The belt diagram serves as a visual map, showcasing the belt’s path and the various components it interacts with. Let’s dissect the key components:
- Crankshaft Pulley: The source of power, driven by the crankshaft’s rotation.
- Alternator: Supplies electrical power to the battery and various electrical components.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant throughout the engine, preventing overheating.
- Power Steering Pump: Assists in steering the vehicle.
- Tensioner: Maintains proper belt tension, ensuring smooth operation and preventing slippage.
In addition to the above, your 2010 Focus 2.0 may use an accessory belt, which typically drives less essential components like the air conditioning compressor.
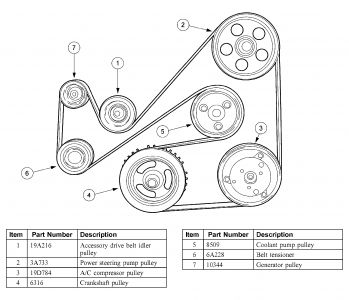
Image: www.fixya.com
Navigating Maintenance: Tips for Belt Replacement
Identifying Signs of Wear and Tear: When to Replace the Belt
Belts, like any mechanical part, wear down over time. Recognizing the signs of belt deterioration is essential for preventing breakdowns. Common indicators include:
- Cracking or fraying: Visible damage like cracks or fraying on the belt surface indicates significant wear.
- Slipping or squealing: A slipping or squealing sound, particularly during engine acceleration or deceleration, suggests inadequate belt tension.
- Excessive vibration: A noticeable vibration originating from the engine area could point to a failing belt or tensioner.
Proactive Maintenance: Ensuring Optimal Engine Performance
Regular belt inspections are crucial for maintaining peak engine performance. It is recommended to visually inspect the belt every 3-6 months. If you discover any signs of wear or tear, it’s essential to replace the belt promptly. Don’t wait for a complete breakdown!
Belt Replacement: A DIY Guide or a Mechanic’s Touch?
For most individuals with a basic mechanical aptitude, replacing a belt can be a DIY project. However, accessing the belt on a 2010 Focus 2.0 might require removing other engine components. If you feel uncomfortable tackling this task, consulting a qualified mechanic is always a safer and more efficient choice.
FAQs About the 2010 Ford Focus 2.0 Belt Diagram
1. What is the recommended belt replacement interval for a 2010 Ford Focus 2.0?
While manufacturers suggest replacing the belt every 60,000 miles, it’s always best to consult your owner’s manual for the specific recommendations for your vehicle.
2. How can I check the belt tension?
A simple visual inspection often suffices. Feel the belt and check for any looseness. However, a more accurate method involves using a tension gauge to measure the belt’s deflection.
3. Are there different types of belt materials?
Yes. Serpentine belts are typically made of rubber. However, some modern vehicles utilize belts made from a blend of rubber and other materials to enhance durability and heat resistance.
4. Is it safe to use generic belts on my 2010 Ford Focus 2.0?
While generic belts are readily available, it’s vital to use belts that meet the specific requirements for your vehicle. Opting for OEM or reputable aftermarket belts will ensure compatibility and long-term performance.
2010 Ford Focus 2.0 Belt Diagram
Conclusion
The 2010 Ford Focus 2.0 belt diagram isn’t a mystery anymore. Armed with this knowledge, you can confidently approach belt maintenance and ensure your engine continues to run smoothly. Remember, a well-maintained belt system is crucial for optimal engine performance and longevity.
Are you interested in further exploring the details of 2010 Ford Focus 2.0 engine maintenance? Leave a comment below and let us know what you’d like to learn next!






