Remember those clunky chemistry textbooks from high school, filled with diagrams of atoms and incomprehensible equations? They left me with a foggy understanding of the fundamental building blocks of matter. It wasn’t until I started working on a real-world project involving material science that I realized how important a solid grasp of atomic structure, ions, and isotopes was. This knowledge became my secret weapon, allowing me to understand the properties of materials and predict their behavior. From then on, my chemistry vocabulary transformed from a jumbled mess to a concise and powerful tool.
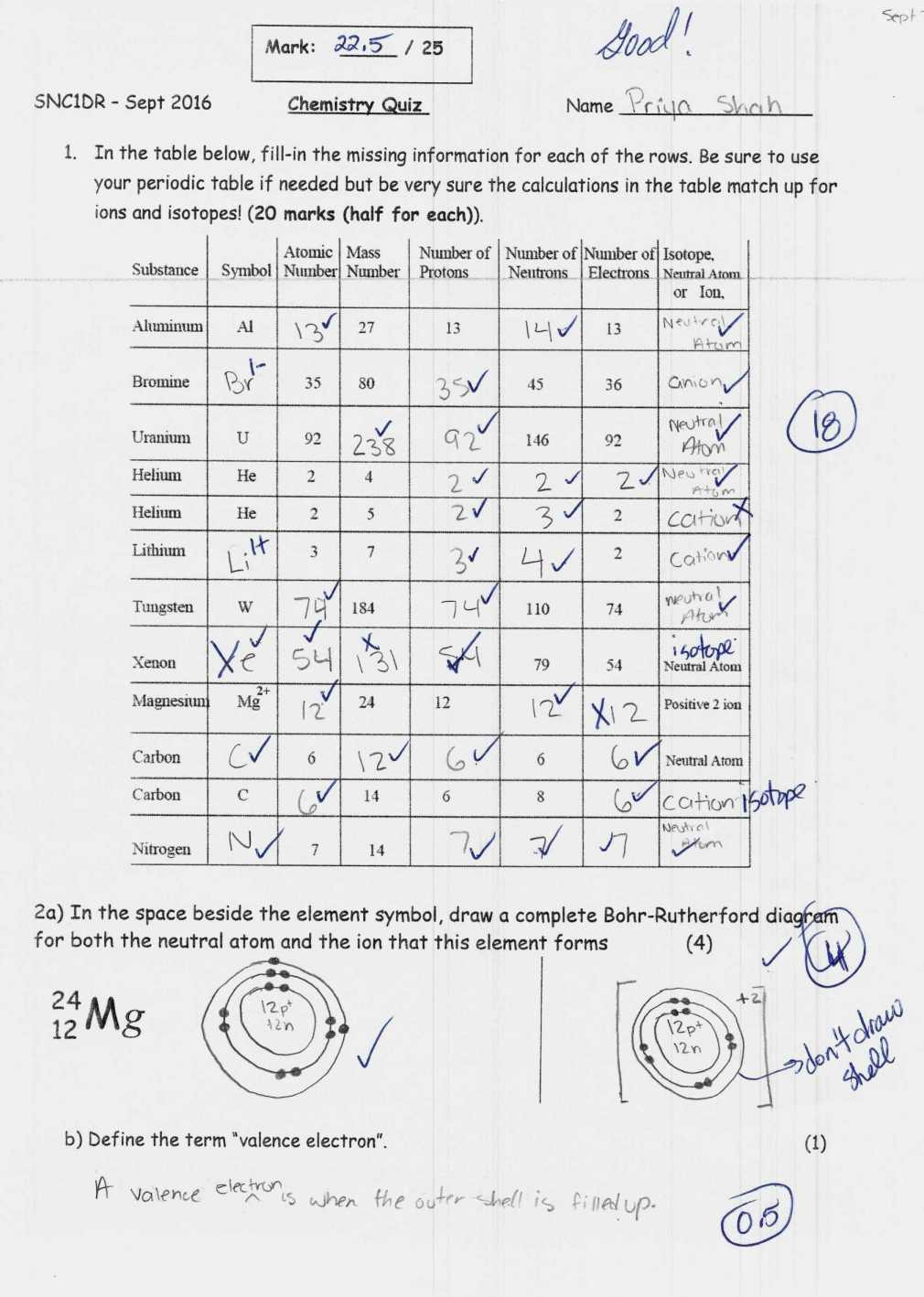
Image: learningschoollisa.z13.web.core.windows.net
Today, I’m excited to share the journey of understanding the fundamental components of matter with you! Whether you’re a high school student tackling chemistry for the first time or a seasoned scientist seeking a refresher, this blog post is your guide to unlocking the secrets of atoms, ions, and isotopes. Just like the proverbial key that opens the door to a treasure trove of knowledge, this post is your key to grasping the inner workings of our physical world.
Navigating the Atomic Landscape: Unraveling the Structure
At its core, an atom is the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. Imagine it as a miniature solar system, with a positively charged nucleus at its center surrounded by negatively charged electrons in orbit. The nucleus itself is composed of protons and neutrons, packed tightly together like a tiny, dense ball.
Protons, carrying a positive charge, determine the element’s identity. Each element has a unique number of protons, known as its atomic number. For example, all carbon atoms have six protons, whereas all oxygen atoms have eight. Neutrons, carrying no charge, contribute to the atom’s mass. They can vary within a single element, making up different isotopes of the element.
The Dynamics of Charge: Understanding Ions
Atoms are typically electrically neutral, meaning they have an equal number of protons and electrons. However, atoms can gain or lose electrons through interactions with other atoms, resulting in the formation of charged particles called ions.
When an atom gains an electron, it becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. For example, when a chlorine atom gains an electron, it becomes a chloride ion (Cl–). Conversely, when an atom loses an electron, it becomes positively charged and is called a cation. For example, when a sodium atom loses an electron, it becomes a sodium ion (Na+).
The Enigma of Isotopes: Exploring Variations Within Elements
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons in their nuclei. Since only the number of protons determines the element’s identity, isotopes share the same atomic number, but they have different atomic masses due to their differing neutron counts.
For instance, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon. Both have six protons, but carbon-12 has six neutrons, while carbon-14 has eight. This difference in neutron number results in slightly different properties for each isotope. Carbon-14, with its extra neutrons, is radioactive and has a half-life of 5,730 years, making it a valuable tool for dating ancient artifacts.
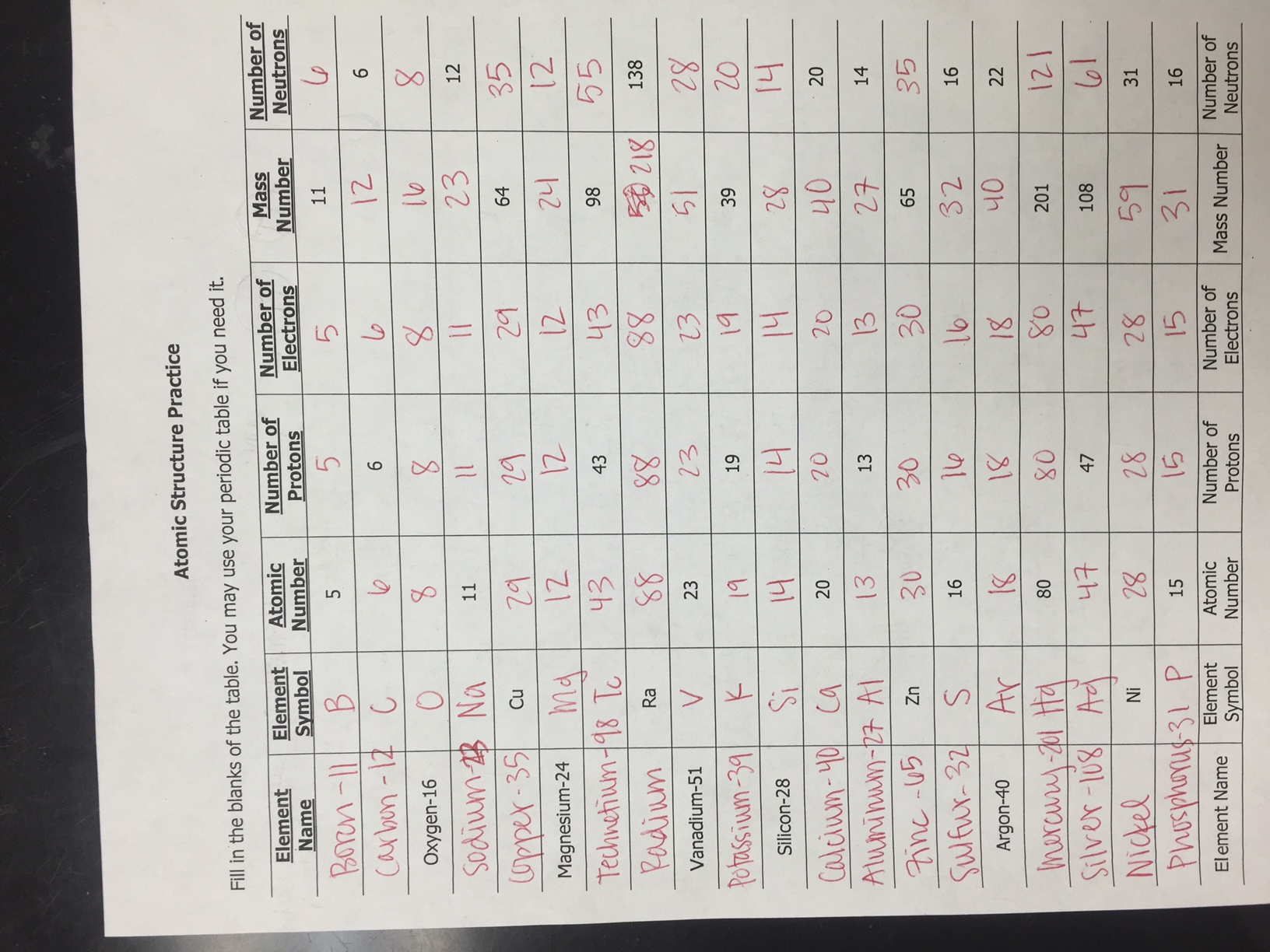
Image: hollphysicalscience.weebly.com
Making Sense of It All: Putting Atomic Structure, Ions, and Isotopes Together
Understanding the interplay between atomic structure, ions, and isotopes is crucial for grasping the behavior of matter. The arrangement of electrons in an atom’s orbital determines its chemical reactivity, leading to the formation of bonds between atoms and the creation of molecules. Furthermore, the relative abundance of isotopes of a given element influences its properties and behavior. For example, the abundance of the radioactive isotope carbon-14 in the atmosphere is used to date fossilized remains and archaeological artifacts.
While the concept might seem abstract at first, think of it like a puzzle. Each piece – atomic structure, ions, and isotopes – interlocks, contributing to the complete picture of how matter behaves. This knowledge empowers us to understand processes like chemical reactions, nuclear energy, and the formation of different elements in the universe.
Mastering the Concepts: Essential Tips and Expert Advice
To truly grasp the concepts of atomic structure, ions, and isotopes, it’s essential to move beyond rote memorization and delve deeper into understanding the underlying principles. Here’s a list of tips and expert advice to get you started:
- Visualize: Draw diagrams of atoms with their protons, neutrons, and electrons. This visual representation will help you solidify your understanding of their arrangement and how they interact.
- Practice, practice, practice: Work through numerous worksheets and problems designed to test your knowledge of atomic structure, ions, and isotopes. This repetitive practice will reinforce your understanding and develop your problem-solving skills.
- Seek connections: Connect the concepts of atomic structure, ions, and isotopes to real-world examples. Explore how these concepts play a role in technologies like batteries, nuclear energy, and medicine.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some of the frequently asked questions about atomic structure, ions, and isotopes:
Q: What is the difference between an atom and an ion?
A: An atom is a neutral particle with an equal number of protons and electrons. An ion is a charged particle formed when an atom gains or loses electrons.
Q: How are ions formed?
A: Ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. This process is called ionization.
Q: What is the importance of isotopes?
A: Isotopes play a crucial role in various fields like archaeology (radioactive carbon dating), medicine (medical imaging), and nuclear energy.
Atomic Structure Ions And Isotopes Worksheet
Unlocking the World of Atoms: Your Next Steps
The journey of understanding the microscopic world of atoms, ions, and isotopes is a journey of constant exploration and discovery. By taking the time to grasp the fundamental concepts and practice diligently, you unlock a world of possibilities. Remember, you are not alone in this pursuit of knowledge. There are numerous resources available online, in libraries, and through tutoring centers to help you along the way.
Are you interested in delving deeper into the fascinating world of atomic structure, ions, and isotopes? Leave a comment below and share your thoughts. Let’s continue this discussion together!






