Please provide me with some context or a question for me to respond to. I need more information to be able to give you a helpful answer.
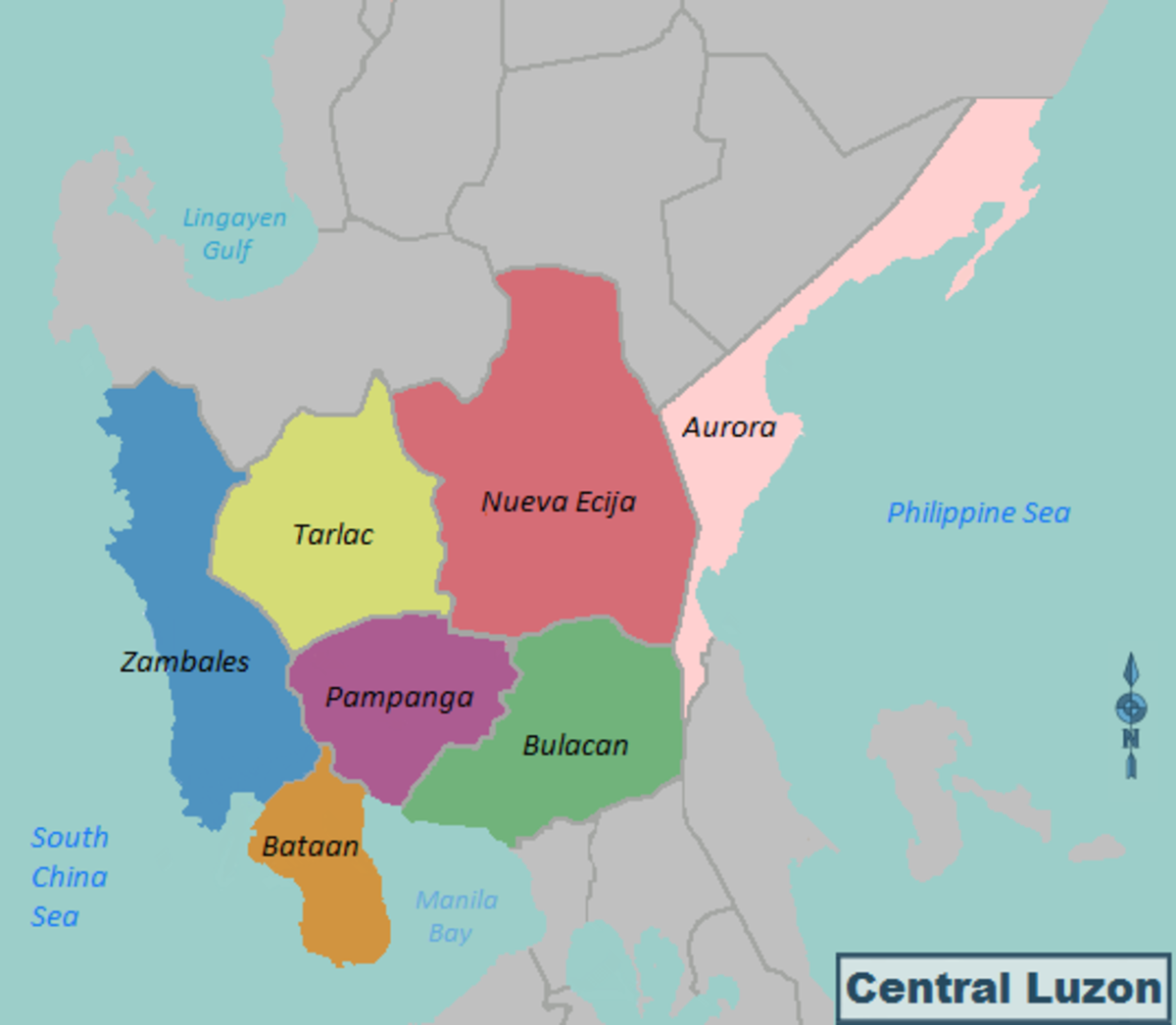
Image: www.vrogue.co
For example, you could ask me:
- “What is the capital of France?”
- “Write a short story about a cat who can talk.”
- “Explain the concept of quantum superposition.”
- “Can you provide me with some information about the history of the internet?”
I am ready to assist you!
Let’s talk about artificial intelligence.
What are some of the ethical considerations we need to address as AI technology continues to develop?
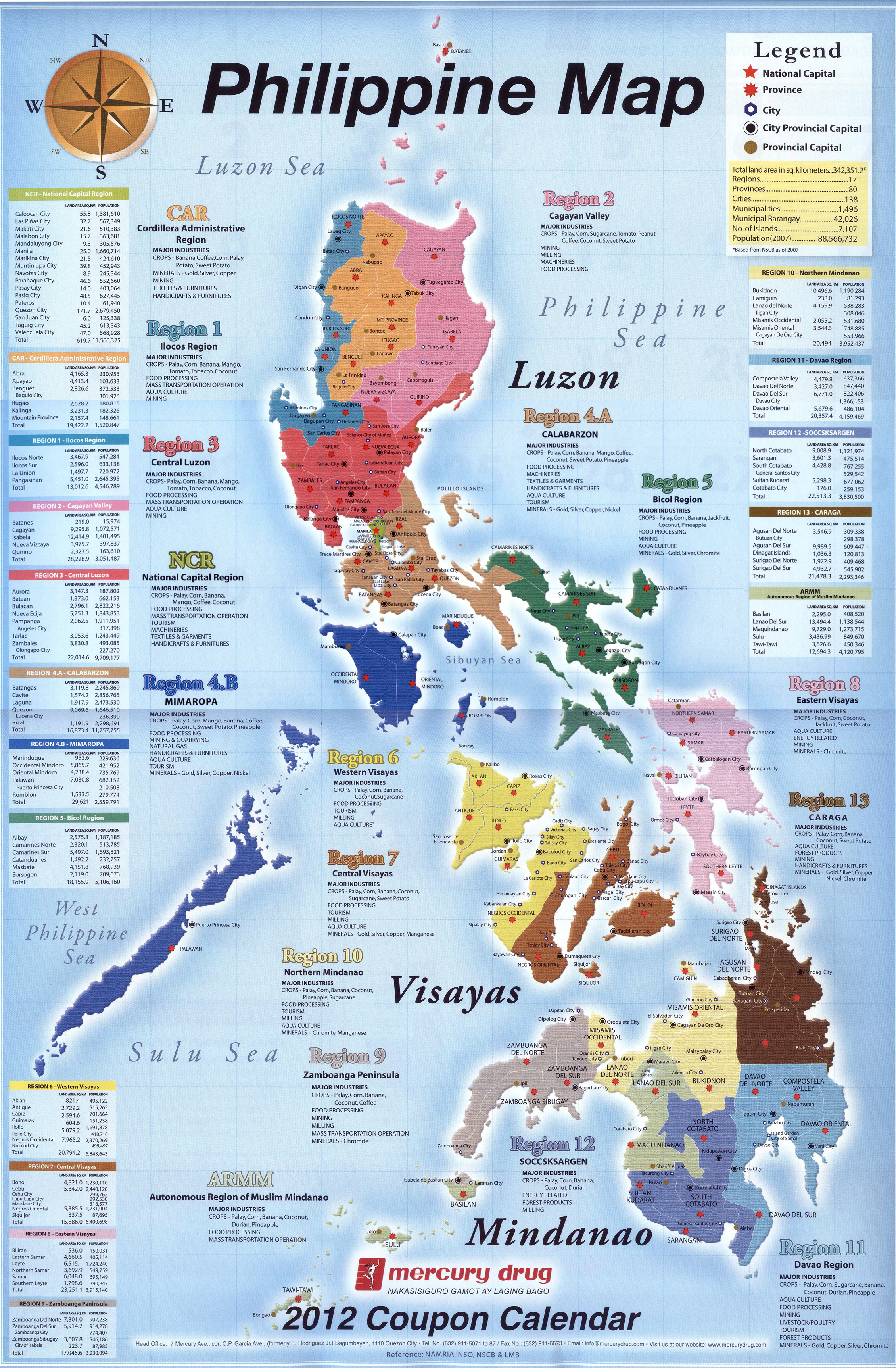
Image: worldmap-64870f.netlify.app
List Of Provinces Of The Philippines
As AI technology races forward, it’s essential to examine its ethical implications. The following are some key areas of concern that require careful consideration and proactive measures:
1. Bias and Discrimination:
- Data Bias: AI models trained on biased datasets can perpetuate and amplify existing social inequalities. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes in areas like hiring, loan approvals, and criminal justice.
- Algorithmic Bias: Even if data is unbiased, the algorithms themselves can introduce biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory treatment.
2. Job Displacement and Economic Impact:
- Automation of Tasks: AI is automating tasks across various industries, leading to job displacement. This raises concerns about unemployment, income inequality, and the need for retraining programs.
- Economic Disparity: The benefits of AI may not be equally distributed, widening the gap between those who can leverage it and those who are left behind.
3. Privacy and Security:
- Data Privacy: AI applications often require vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about data breaches, misuse, and the right to privacy.
- Security Risks: AI systems can be vulnerable to hacking, manipulation, and misuse, posing a threat to national security, critical infrastructure, and personal safety.
4. Transparency and Explainability:
- Black Box Problem: Many AI models are complex and opaque, making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their decisions. This lack of transparency can hinder accountability and trust in AI.
- Explainability: Developing methods to explain AI decisions is crucial for building trust, addressing biases, and ensuring fairness.
5. Responsibility and Accountability:
- Liability: Who is responsible when AI systems make mistakes or harm people? Establishing clear legal frameworks for AI responsibility is essential.
- Ethical Guidelines: Developing ethical guidelines for AI development and deployment is necessary to ensure responsible and accountable use.
6. Weaponization and Autonomous Weapons:
- Autonomous Weapons Systems: The development of AI-powered weapons raises ethical concerns about the potential for unintended consequences and the possibility of AI systems making life-or-death decisions.
- Human Control: Ensuring that humans maintain control over AI systems, particularly in sensitive domains like weaponry, is a crucial priority.
7. Impact on Human Identity and Meaning:
- Dependence on AI: As we become increasingly reliant on AI, there are concerns about the potential for AI to erode human agency, creativity, and critical thinking skills.
- Human-AI Interactions: Understanding the ethical and social implications of human-AI interactions, especially in areas like education, healthcare, and companionship, is essential.
Addressing these ethical considerations requires collaborative efforts from various stakeholders, including governments, researchers, industry leaders, and civil society. Establishing strong ethical frameworks, promoting transparency and accountability, and actively addressing these issues will be crucial for harnessing the power of AI for the benefit of humanity.






