Have you ever wondered why a ball thrown in the air eventually comes back down? Or why a car needs to be pushed to get it moving? These seemingly simple questions are actually the building blocks of understanding the world around us. The answers lie in the fundamental concepts of forces and motion, which govern everything from the movement of planets to the actions of everyday objects.
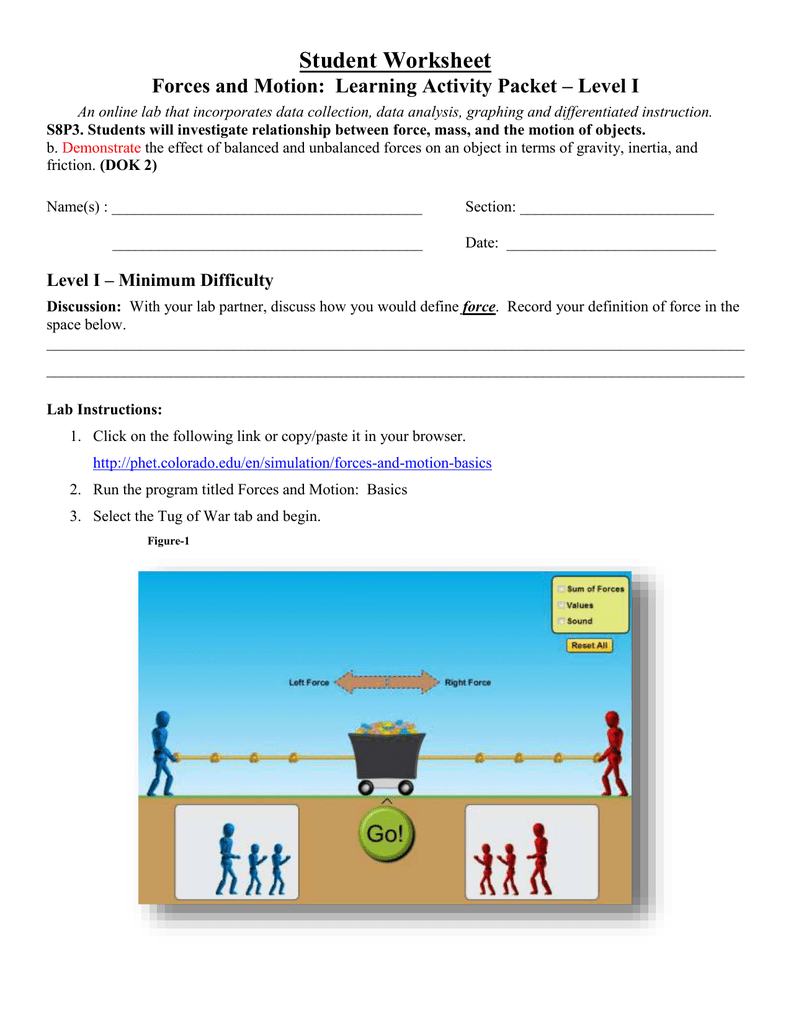
Image: erinprinkin.blogspot.com
Forces and motion are essential for comprehending how things move, interact, and change within our universe. This knowledge opens the door to understanding not just the physics of our surroundings but also the engineering marvels that shape our lives, like cars, airplanes, and even the simple act of walking.
Understanding Forces
Defining Forces
A force is simply a push or pull that can change an object’s motion. It’s an invisible influence that can set an object in motion, stop it, or change its direction. Forces are measured in units called Newtons (N), named after the great physicist Sir Isaac Newton.
Types of Forces
There are many types of forces at play in the universe, but some of the most common include:
- Gravitational Force: The force that attracts objects towards each other, responsible for keeping us grounded and keeping planets in orbit around the sun.
- Friction Force: The force that resists motion between two surfaces in contact, like the friction between your shoes and the ground as you walk or between the tires of a car and the road.
- Normal Force: The force exerted by a surface that supports an object, like the force of the floor pushing up on you to prevent you from falling through it.
- Applied Force: The force applied directly to an object, like the force you exert when pushing a door open or throwing a ball.
- Magnetic Force: The force exerted by magnets on other magnetic materials or on moving charges.
- Electrostatic Force: The force exerted by electric charges on each other.

Image: athensmutualaid.net
Motion and Its Principles
What is Motion?
Motion is simply the change in position of an object over time. It can be described in terms of its speed, direction, and acceleration.
Speed and Velocity
Speed is the rate at which an object moves, measured by the distance traveled in a given time. Velocity, on the other hand, is the rate of change in position, and it includes both speed and direction. For example, a car traveling at 60 mph is moving at a certain speed, but its velocity is also influenced by its direction of travel – north, south, east, or west.
Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes over time. This change can be either an increase in speed, a decrease in speed, or a change in direction. A car accelerating from rest is experiencing a change in speed, while a car taking a corner at a constant speed is experiencing a change in direction, and therefore, acceleration.
Newton’s Laws of Motion
The fundamentals of forces and motion are best explained through Newton’s Laws of Motion, three fundamental principles that govern the behavior of objects in motion. These laws, discovered by Sir Isaac Newton in the 17th century, provide a foundation for understanding the mechanics of our world.
Newton’s First Law: Inertia
Newton’s First Law, also known as the Law of Inertia, states that an object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This means that objects have a tendency to resist changes in their motion.
Newton’s Second Law: Force and Acceleration
Newton’s Second Law describes the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. It states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass. Simply put, a larger force results in a greater acceleration, and a heavier object will require a larger force to accelerate at the same rate.
Newton’s Third Law: Action and Reaction
Newton’s Third Law, commonly known as the Law of Action and Reaction, states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When you push against a wall, the wall pushes back on you with an equal force. While you may only feel the force you exert, the wall is also experiencing a force from your push. This law explains why jumping on a trampoline produces an upward force, why a rocket propels itself forward by expelling gases backward, and why you feel a recoil when firing a gun.
Everyday Applications of Forces and Motion
The concepts of forces and motion are not just theoretical constructs. They are deeply ingrained in our daily lives, shaping our experiences and empowering us to create amazing technologies. Here are a few examples:
- Transportation: Cars, airplanes, ships, trains, and bicycles all rely on forces and motion principles. Engines generate forces to move the vehicle, and the vehicle’s motion is influenced by factors like friction and air resistance.
- Sports: From hitting a baseball to kicking a soccer ball, every sport involves forces and motion. Athletes use their bodies to generate forces that propel objects, and they use their understanding of these forces to improve their performance.
- Building and Construction: Structures like buildings, bridges, and roads must be built to withstand the forces of gravity, wind, and other external factors. Engineers use their knowledge of forces and motion to design these structures to ensure safety and durability.
- Medical Devices: From pacemakers to artificial limbs, medical devices often rely on forces and motion principles. For example, prosthetic legs use actuators to generate forces that allow the wearer to walk, and pacemakers use electrical impulses to regulate the heart’s beating motion.
Forces And Motion Basics Answer Key
Conclusion
Understanding the fundamentals of forces and motion is crucial for navigating and shaping our physical world. From the simple act of walking to the advanced engineering that drives our modern society, forces and motion are the invisible forces that shape our experiences. This article has provided a foundational understanding of these concepts, including their definition, important principles, and practical applications. Keep exploring the fascinating world of physics, and you’ll continue to uncover new wonders within the forces and motions that govern our universe.






