Remember that time in chemistry class when we were tasked with figuring out the unknown concentration of a solution? I was staring at the burette, feeling a mix of confusion and excitement. It was our first acid-base titration experiment, and it felt like magic watching the color change as the solution was slowly neutralized. While the process can be daunting at first, it’s an essential technique in chemistry, and mastering it is crucial for success in the lab. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the components of a successful acid-base titration lab report and provide you with tips for making the process a breeze.

Image: www.vrogue.co
Understanding how to write a compelling titration lab report isn’t just about getting a good grade; it’s about demonstrating your grasp of the concepts, your ability to analyze data, and your skills in scientific communication. Whether you’re a student tackling your first lab or a seasoned researcher looking for a refresher, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to craft a top-notch lab report.
Understanding Acid-Base Titration: The Fundamentals
What is Acid-Base Titration?
Acid-base titration is a quantitative chemical analysis technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution (analyte) by reacting it with a solution of known concentration (titrant). It relies on the principle of neutralization – the reaction between an acid and a base to form salt and water.
The Key Players in Acid-Base Titration:
- Analyte: The solution of unknown concentration that you want to determine.
- Titrant: The solution of known concentration that is added to the analyte.
- Indicator: A substance that changes color when the reaction reaches the equivalence point, indicating the neutralization of the analyte.
- Equivalence Point: The point in the titration where the moles of acid and base are equal, resulting in a complete reaction.
- Endpoint: The point in the titration where the indicator changes color, providing a visual signal of the equivalence point.
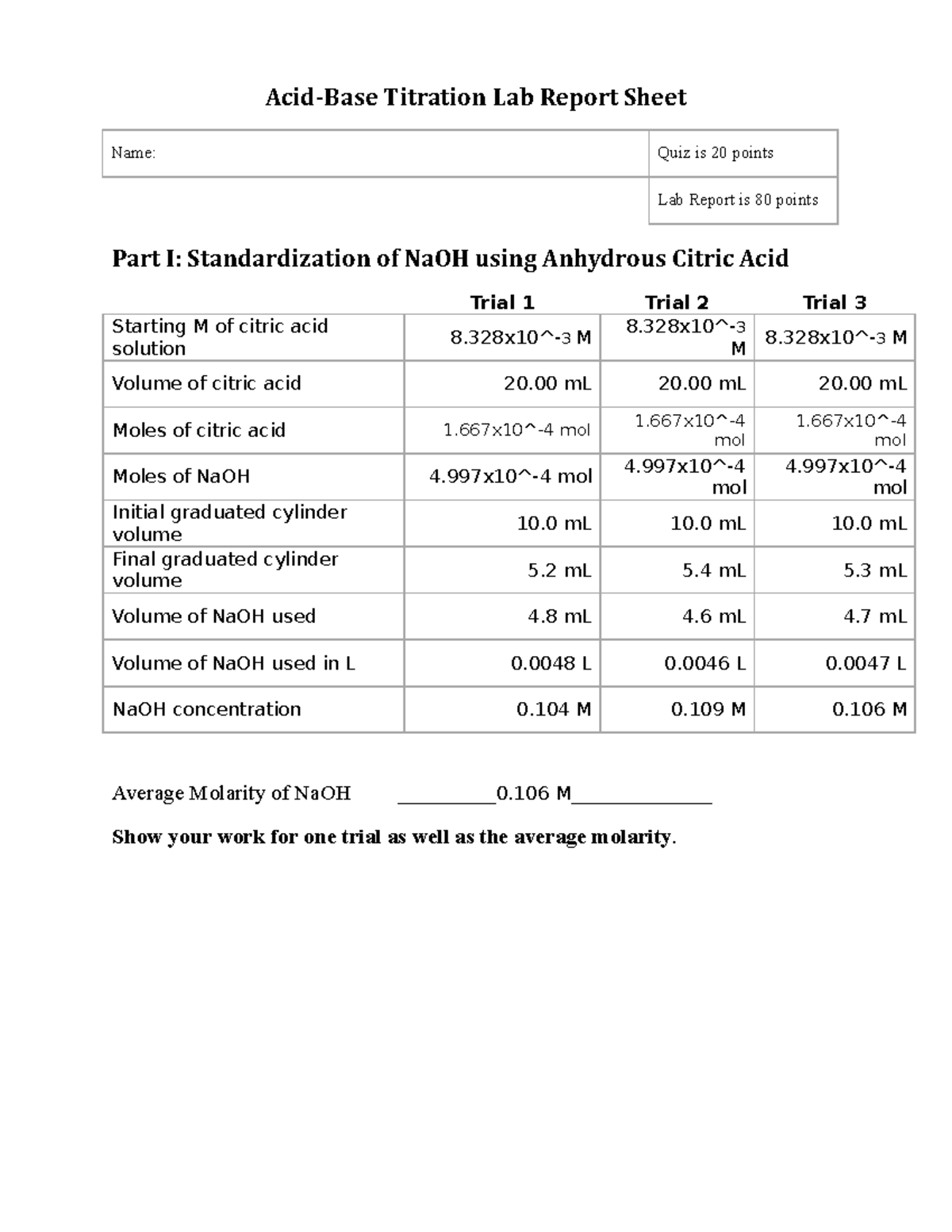
Image: emerykruwmacias.blogspot.com
The Steps Involved in Acid-Base Titration:
- Preparation: Carefully prepare the analyte and titrant solutions, ensuring their concentrations are known accurately.
- Titration Setup: Set up the titration apparatus, which typically consists of a burette, a flask containing the analyte, and a magnetic stirrer.
- Titration Process: Slowly add the titrant to the analyte while continuously stirring, carefully observing the indicator’s color change.
- Endpoint Determination: Stop the titration at the endpoint, which signifies that the analyte has been completely neutralized.
- Data Analysis: Record the volume of titrant used to reach the endpoint and use stoichiometry to calculate the analyte’s concentration.
Navigating the Acid-Base Titration Lab Report: A Step-by-Step Guide
A well-structured lab report is essential for effectively communicating your experimental results and understanding the scientific process. Here’s a breakdown of the essential sections of an acid-base titration lab report, along with essential tips for each part:
1. Title:
The title should accurately and concisely encapsulate the experiment’s purpose. For example: “Determination of the Concentration of an Unknown Acid by Titration.” Avoid generic titles.
2. Objective:
State the specific goals of the experiment. What is the purpose of the titration? What are you trying to determine? This section should be clear and concise, outlining the experiment’s aim.
3. Introduction:
Provide background information about acid-base titrations. Discuss the theory and principles behind the technique. This includes explaining acid-base reactions, stoichiometry, and the concept of neutralization. If your experiment involves any specific acid or base, briefly introduce their properties.
4. Materials and Methods:
List all materials and equipment used in the experiment. This includes chemicals, glassware, instruments, and any safety equipment. Describe the experimental procedure in detail, step-by-step. Be precise and clear. Provide sufficient information so that another researcher could replicate your experiment.
5. Results and Data Analysis:
Clearly present your collected data. Use tables for organizing raw data (volume of titrant used, endpoint determination). Present calculated results, including the concentration of the unknown analyte, with appropriate units and significant figures. Include any graphs or plots (e.g., titration curve) that help visually represent your data.
6. Discussion:
Interpret your results. Analyze your data, addressing the objective of the experiment. Compare your findings to theoretical values (if available) and discuss any discrepancies. Suggest possible sources of errors and how they might have impacted your results. Discussing the significance of your findings within the context of the topic is essential.
7. Conclusion:
Summarize your findings and discuss the success of your experiment. State whether you achieved the objectives of the titration. Briefly reiterate the key conclusion drawn from your analysis. It should demonstrate your understanding of the experiment’s results and their implications.
8. References:
List any sources of information used in the report, including textbooks, research articles, and online resources.
Tips and Best Practices for Writing Effective Titration Reports
Remember, a well-written lab report isn’t merely a list of observations; it’s a scientific story. Here are some tips to enhance the quality of your titration lab reports:
- Thorough Data Collection: Carefully record all your observations and data during the experiment. Ensure all measurements are accurate and include proper units.
- Data Analysis and Interpretation: Use statistical analysis tools (e.g., mean, standard deviation) to interpret your data. Be able to identify trends and draw meaningful conclusions from your results. Don’t just present the numbers; explain what they mean in the context of your experiment.
- Clear and Concise Language: Write in a clear, concise, and objective style. Avoid jargon. Use precise technical language to describe the procedures and results but ensure it’s understandable for a reader without specialized knowledge.
- Visual Aids: Incorporate graphs, charts, and tables to visually represent your data. These aids make your report more engaging and facilitate understanding. Choose appropriate visual presentations that suit your particular dataset.
- Proofreading: Proofread your report thoroughly for errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation. A well-presented report shows your attention to detail.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How can I determine the endpoint of a titration?
The endpoint is reached when the indicator changes color, signifying that the solution has been neutralized. The choice of indicator plays a key role in determining the endpoint. Different indicators change color at different pH values, so selecting the right indicator is important for your experiment.
2. What are the common sources of error in titration?
Common sources of error include inaccurate measurements of the analyte or titrant, improper indicator selection, incomplete mixing, and parallax error during volume readings. Addressing these potential sources of error helps improve the accuracy of your results.
3. What are the applications of acid-base titration in real-world settings?
Acid-base titrations have broad application in various fields like environmental monitoring, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and food science. For instance, they are used to analyze water quality, determine soil acidity, and analyze the active ingredients in pharmaceuticals and food products.
Acid Base Titration Lab Report Pdf
Conclusion
Mastering the art of acid-base titrations is a valuable skill for any aspiring chemist or scientist. Remember, understanding the theory, following a systematic approach, and presenting data in a clear and concise manner are key. Are you interested in learning more about specific applications of acid-base titration or want to explore advanced titration techniques? Let us know in the comments below!






