Ever wondered what makes concrete so strong that it can support massive structures, from towering skyscrapers to sprawling bridges? It all boils down to a carefully crafted mix of ingredients, and the mix ratio plays a crucial role in determining the final strength of concrete, measured in pounds per square inch (psi). Among the various strengths, 3000 psi concrete stands out as a versatile choice for numerous residential and commercial projects. But what exactly goes into achieving that 3000 psi mark, and how can you ensure consistent results?
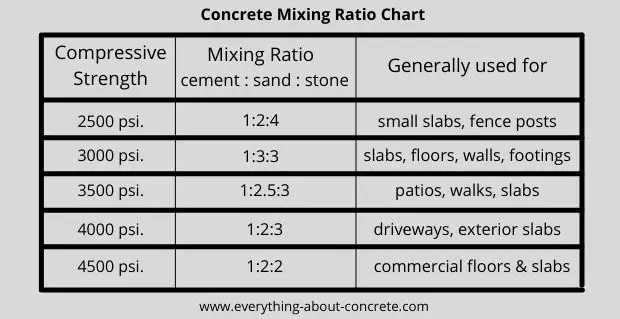
Image: edmontonrealestateinvestmentblog.com
Understanding the mix ratio for 3000 psi concrete is not just about mixing ingredients randomly. It requires a precise balance of cement, aggregates (sand and gravel), and water. This ratio directly impacts the concrete’s workability, setting time, and ultimately, its compressive strength. This article will delve into the intricacies of mix ratios for 3000 psi concrete, exploring the science behind it, the factors influencing the mix, and practical tips for achieving the desired results.
The Essential Components of Concrete: A Closer Look
Cement: The Binding Force
Cement acts as the binder in concrete, reacting with water to form a hardened matrix that binds the aggregates together. Portland cement is the most commonly used type, offering excellent strength and durability. The amount of cement used directly influences the strength of the concrete. A higher cement content leads to higher strength, but it also increases costs and can sometimes make the concrete more prone to shrinkage.
Aggregates: The Backbone of Strength
Aggregates, encompassing sand and gravel, make up the bulk of concrete. They provide strength, volume, and durability, acting as the backbone of the structure. The choice of aggregates depends on the specific requirements of the project. Fine aggregates (sand) contribute to workability and strength, while coarse aggregates (gravel) provide structural integrity. The grading of aggregates, referring to their particle size distribution, also plays a vital role. A well-graded mix with a proper mix ratio ensures even distribution and enhances the concrete’s strength.

Image: www.pinterest.jp
Water: The Catalyst for Reaction
Water serves as the catalyst for the chemical reaction between cement and aggregates, allowing them to harden. However, it’s crucial to remember that too much water can weaken the concrete by diluting the cement paste, leading to reduced strength. On the other hand, insufficient water can result in a dry, unworkable mix. The water-cement ratio is a critical factor in determining the final properties of concrete, directly affecting its strength, durability, and workability.
Understanding the Mix Ratio for 3000 psi Concrete
A Typical Mix
A standard mix ratio for achieving 3000 psi concrete typically follows a 1:2:3 ratio by volume, encompassing cement, sand, and gravel respectively. This means for every 1 cubic foot of cement, you’ll use 2 cubic feet of sand and 3 cubic feet of gravel. However, this mix ratio can vary depending on multiple factors, including the type of cement, aggregates, water-to-cement ratio, and desired workability.
Factors Influencing the Mix Ratio
Achieving a specific strength like 3000 psi requires careful consideration of various factors.
- Type of cement: Different types of cement have varying strengths. Type I/II Portland cement is commonly used for general construction and can be adjusted to achieve 3000 psi.
- Aggregate properties: The type, size, and grading of aggregates significantly impact the final strength. Using a well-graded mix with robust aggregates is crucial for achieving the desired psi.
- Water-to-cement ratio (w/c ratio): This ratio greatly affects the strength of the concrete. A lower w/c ratio generally leads to stronger concrete but can make the mix less workable.
- Admixtures: Specific admixtures can be added to modify the concrete’s properties, such as its workability, setting time, or strength. Air-entraining admixtures, for instance, improve resistance to freeze-thaw cycles.
- Environmental conditions: Temperature, humidity, and curing conditions can impact the strength development of concrete. Cooler temperatures can slow down the hydration process, affecting the final strength.
Achieving Consistent Results: Practical Tips
Achieving a consistent 3000 psi concrete mix requires more than just following a theoretical ratio. Here are some practical tips:
- Use a reliable source for your materials: Opt for reputable suppliers who deliver high-quality cement, sand, and gravel that meet the project specifications.
- Measure carefully: Accurately measure the ingredients by volume. Avoid using inconsistent measuring tools as it can significantly impact the mix ratio and the strength of the concrete.
- Mix thoroughly: Thorough mixing is crucial to ensure even distribution of the ingredients and achieve a uniform consistency. Use a concrete mixer or, for smaller batches, a shovel or a wheelbarrow for thorough mixing.
- Control the water-to-cement ratio: Adjust the water content based on the desired workability and strength. Too much water weakens the concrete, while too little can make it unworkable.
- Proper curing: Curing is essential for proper strength development. Keep the concrete moist for at least 7 days after pouring, using a curing compound or sheets.
- Testing and analysis: Perform strength tests (compressive strength tests) on samples of the concrete to verify that it meets the required 3000 psi specification.
Mix Ratio For 3000 Psi Concrete
https://youtube.com/watch?v=WcGFQ4B8PSI
Conclusion: Unlocking the Power of 3000 psi Concrete
Understanding the mix ratio for 3000 psi concrete is crucial for achieving the desired strength and durability in a variety of construction projects. By understanding the role of cement, aggregates, and water, and embracing practical tips for consistent mixing, you can ensure the success of your concrete applications. Whether you’re building a patio, foundation, or a more complex structure, mastering the art of 3000 psi concrete allows you to create strong, reliable, and long-lasting structures.
Remember, this is just a starting point. Consult with a qualified concrete professional or engineer for personalized advice and guidance specific to your project’s requirements. They can advise on optimal material selection, mix design, and ensure the concrete you use meets the necessary safety and performance standards.






