Imagine a world where every animal eats the same thing, or where one species suddenly disappears without a trace. Chaos, right? That’s the power of food chains and webs, the interconnected networks that hold ecosystems together. These intricate relationships are a fascinating study in natural balance, and understanding them is key to appreciating the complexity and beauty of the natural world.
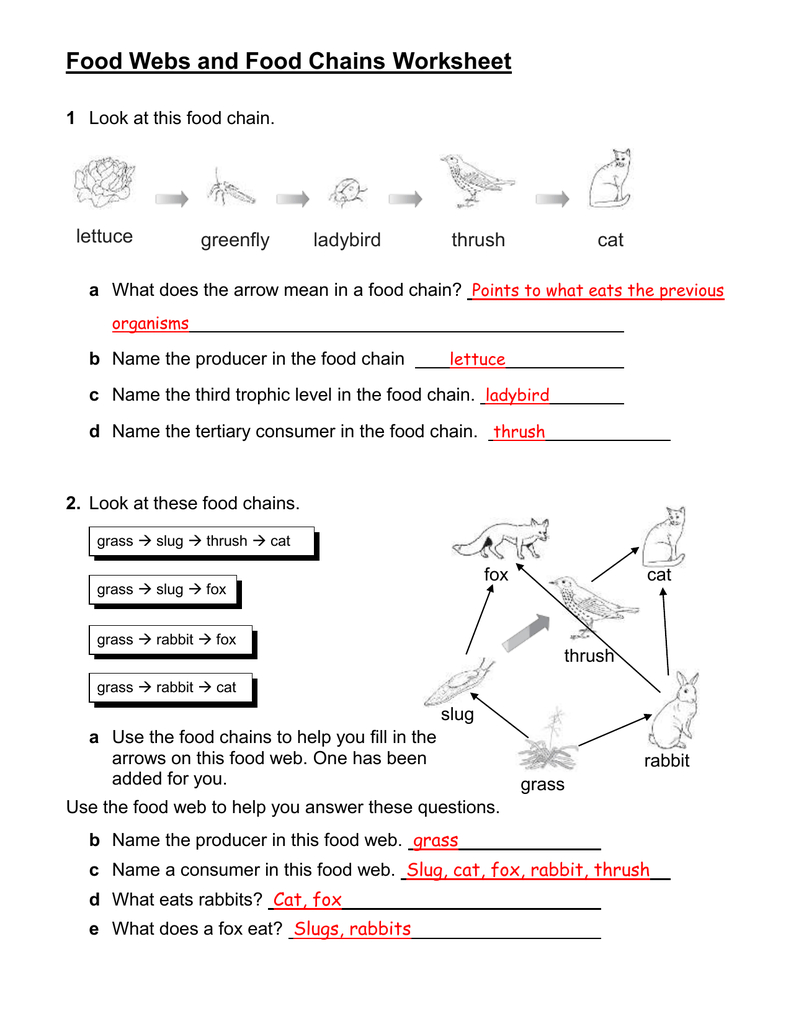
Image: db-excel.com
So, you’ve got a food chains and webs worksheet in front of you, ready to explore the fascinating world of predator and prey, producers and consumers. This guide will walk you through the key concepts, break down complex ideas, and provide you with the answers you need to conquer those worksheets. Get ready to dive deep into the interconnected tapestry of life!
Understanding the Building Blocks: Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers
Producers: The Foundation of the Food Chain
Picture a lush green meadow, vibrant with life. At the base of this ecosystem are the producers, the green plants and algae. They are the masters of photosynthesis, converting sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into energy-rich sugars that fuel their growth. This process is like magic, transforming sunlight into the very essence of life!
Producers are the foundation of every food chain. They provide the initial source of energy for the entire ecosystem, making them the ultimate life-givers. Without producers, the rest of the chain would crumble like a house of cards.
Consumers: The Diverse Diners of the Food Chain
Above the producers stand the consumers, the creatures who rely on other organisms for their meals. Think of a deer grazing in a meadow, its delicate hooves crunching on the lush grass. This herbivore, a primary consumer, gets its energy directly from the producers.
As the food chain climbs higher, we encounter the secondary consumers – the carnivores who feast on herbivores. A wolf stalking a deer is a classic example. And then there are the tertiary consumers, those apex predators that sit at the top of the food chain, like a lion surveying its kingdom.
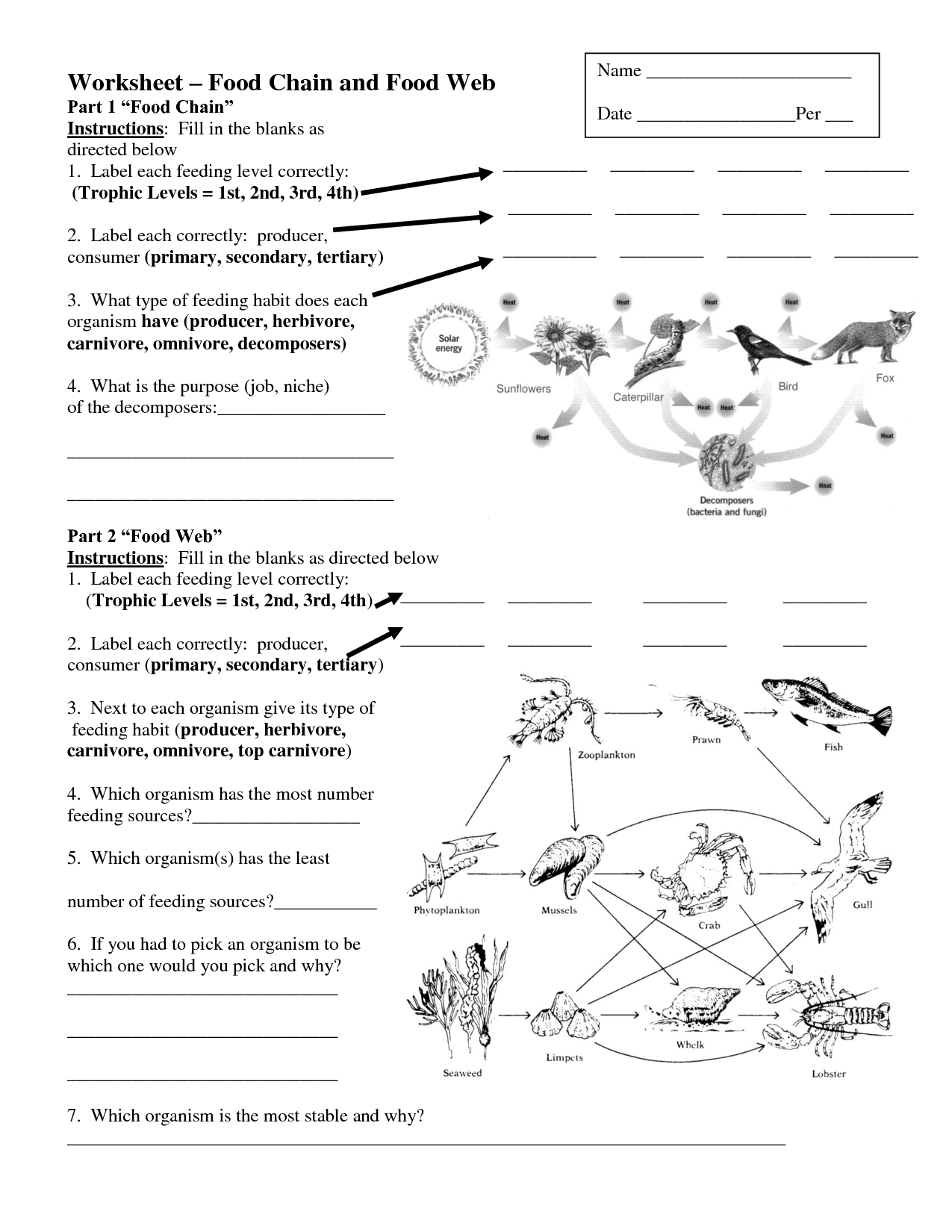
Image: www.worksheeto.com
Decomposers: The Unsung Heroes of the Ecosystem
But the story doesn’t end there! The ecosystem is also home to decomposers, like bacteria and fungi, whose role is often overlooked but crucial. They break down dead organisms and waste products, returning vital nutrients back to the soil. These microscopic marvels ensure that nothing goes to waste, turning death into new life.
Decomposers are the silent recyclers of the ecosystem, ensuring that nutrients are constantly being circulated, fueling the growth of new life. No matter how complex a food chain may seem, it all comes down to these three essential components: producers, consumers, and decomposers.
Weaving the Web: Exploring the Interconnections of Ecosystems
Beyond Linear Chains: Unveiling the Complexity of Food Webs
While food chains provide a simplified view of feeding relationships, food webs paint a more accurate and intricate picture. Food webs illustrate the complex network of energy flow within an ecosystem, showing how multiple species interact through their feeding relationships.
Imagine a spiderweb, strands connecting different points. In a food web, each strand represents a predator-prey relationship, with arrows showing the direction of energy flow. Unlike a food chain, a food web doesn’t follow a straight line. It weaves and branches, showcasing the multiple connections between different organisms.
Why Food Webs Matter: Stability and Resilience in the Face of Change
Food webs are crucial for maintaining the stability and resilience of ecosystems. They allow for flexibility in response to changes, ensuring that if one species declines, others can step in to fill the gap. For example, if a disease wipes out a significant population of rabbits in a forest, the wolves that rely on rabbits for food might switch to hunting mice or deer, preventing a catastrophic collapse.
Food webs also help regulate populations, preventing any single species from becoming dominant and outcompeting others. This balance is essential for maintaining biodiversity, which, in turn, contributes to a healthy and thriving ecosystem.
Food Chains and Webs Worksheet Answers: Unlocking the Secrets
Example Worksheet Problems: Deciphering the Interconnectedness
Most food chains and webs worksheets challenge you to analyze specific examples, identify food chain components, and understand how they relate to each other. Let’s break down some common worksheet problems.
Problem 1: Identifying Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers
You might be presented with a list of organisms and asked to classify them as producers, consumers, or decomposers. Here, your knowledge of their feeding habits comes into play. For example, a sunflower is a producer because it makes its own food through photosynthesis. A rabbit is a consumer because it eats plants. And a mushroom, a decomposer, feeds on decaying matter.
Problem 2: Constructing a Food Chain or Web
Another common task is to create a food chain or web based on a given set of organisms. Here, a bit of creativity and logical thinking comes in handy. You might be asked to sequence a group of animals like grass, grasshopper, frog, snake, and hawk into a food chain. In this case, the order would be grass (producer), grasshopper (primary consumer), frog (secondary consumer), snake (tertiary consumer), and hawk (apex predator).
Problem 3: Analyzing the Impact of Changes on the Ecosystem
A more challenging question might ask you to analyze the potential impact of an event on a food web. For instance, you might be asked what would happen if a disease wiped out a large portion of the fish population. This scenario would involve understanding how the loss of fish would affect the species that prey on fish, and the species that rely on those predators. This type of analysis brings to light the delicate balance and interdependency of all living things within an ecosystem.
Mastering the Worksheet: Tips and Tricks for Success
To ace your food chains and webs worksheet, remember these key tips:
- Understand the Basics: Before tackling any specific questions, ensure you have a firm grasp of the key concepts: producers, consumers, decomposers, food chains, and food webs.
- Visualize the Relationships: Draw simple diagrams or food webs to help you visualize the connections between organisms. This aids in understanding the flow of energy and how changes in one part of the ecosystem can impact others.
- Think Critically: When analyzing scenarios, consider the potential consequences of change. Analyze how a decrease or increase in one population could affect the entire ecosystem.
- Practice, Practice, Practice: The more you work with examples and analyze different scenarios, the better you will grasp the intricate workings of food chains and webs.
Beyond the Worksheet: The Importance of Food Webs in Real Life
The study of food chains and webs isn’t just about academic exercises. It has far-reaching implications for understanding and protecting the natural world. From conservation efforts to managing fisheries, understanding food webs is vital for making informed decisions about how we interact with the environment.
Conservation: Protecting the Interconnectedness of Life
Understanding food webs is critical for conservation efforts. By studying the intricate relationships between species, scientists can identify which species are most vulnerable and take steps to protect them. For example, if a keystone species (a species with a disproportionately large impact on the ecosystem) is being threatened, conservationists can focus on protecting its habitat, ensuring the entire food web won’t be destabilized.
Fisheries Management: Ensuring Sustainable Harvesting
Food webs play a crucial role in fisheries management, helping us understand how overfishing can impact the delicate balance of marine ecosystems. By studying the feeding relationships between different fish species, scientists can set sustainable fishing quotas that prevent the collapse of entire populations and allow ecosystems to thrive.
Food Chains And Webs Worksheet Answers
In Conclusion: Unraveling the Tapestry of Life
Food chains and webs worksheets are more than just academic exercises; they provide a window into the fascinating and complex interplay of life on Earth. By understanding these intricate relationships, we gain a profound appreciation for the interconnectedness of all living things and the delicate balance that sustains our planet. So, the next time you see a bird soaring high above, a fish darting through the water, or a mushroom sprouting in the forest, remember that you are witnessing a thread within the grand tapestry of nature. Keep exploring, keep learning, and keep cherishing the wonder of our shared ecosystem!






