Have you ever wondered how a tiny seed can grow into a towering oak tree, or how a playful squirrel can scamper through the branches, its belly full of acorns? The answer lies in the delicate dance of life that plays out in every ecosystem on Earth – a dance orchestrated by food chains, food webs, and the intricate pyramid of energy. In this exploration, we’ll embark on a journey to understand these fundamental concepts and learn how they shape the world we live in.
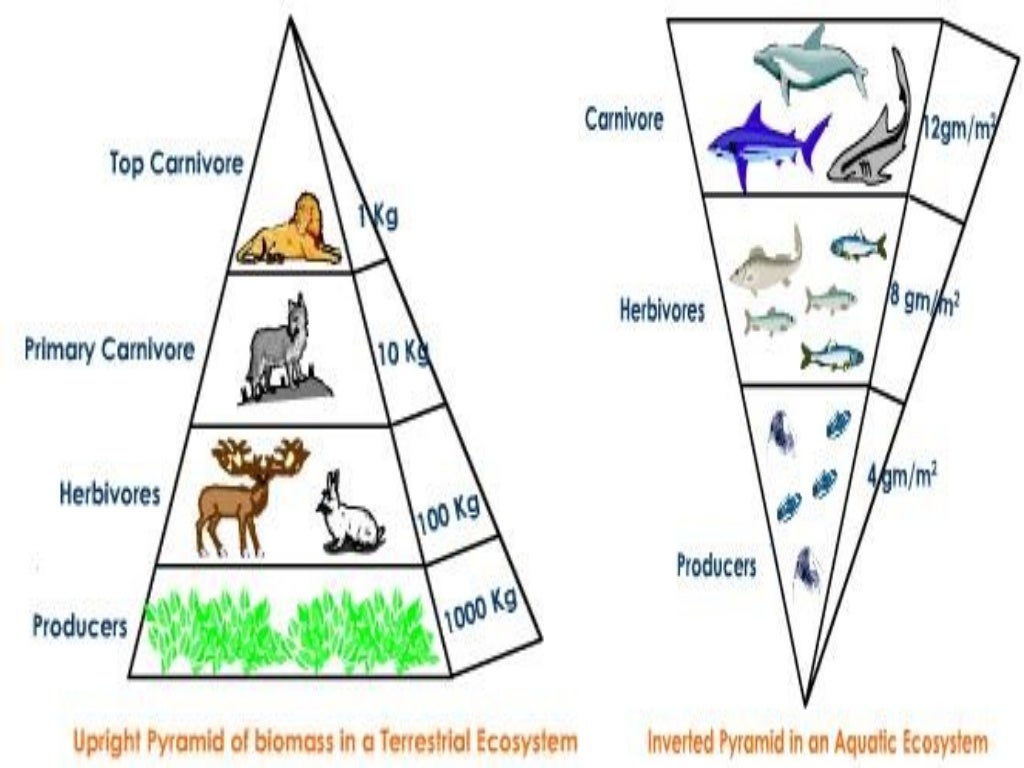
Image: www.babezdoor.com
From the tiniest bacteria to the largest whales, all living organisms are connected in a complex web of interdependence. Food chains and food webs provide the framework for this intricate relationship, revealing how energy flows through ecosystems and ensures the survival of every living thing. While food webs illustrate the complex tapestry of connections, the energy pyramid acts as a visual tool to understand the transfer and dissipation of energy among different trophic levels. Let’s dive deeper!
Understanding Food Chains: A Linear Journey of Energy
Imagine a simple line of dominoes, each one falling into the next. That’s how a food chain works – a linear sequence where energy flows from one organism to another. It’s a single pathway that depicts the feeding relationships among organisms within an ecosystem.
At the base of the food chain lie the producers – plants and algae that capture energy from sunlight through photosynthesis. These organisms are the primary source of food and energy for all other living things. Next come the herbivores – animals that consume producers and obtain energy from them. Herbivores are then eaten by carnivores, animals that feed on other animals. The chain may continue with secondary carnivores that feed on other carnivores.
Here’s a simple food chain example that illustrates this flow:
- Sun
- Grass (Producer)
- Grasshopper (Herbivore)
- Frog (Carnivore)
- Snake (Secondary Carnivore)
- Hawk (Top Predator)
Food Webs: Interwoven Connections in a Complex Ecosystem
As we move beyond the simple food chain, we encounter the intricate world of food webs. Food webs are interconnected food chains, demonstrating the complex network of interactions within an ecosystem. It’s like a bustling marketplace where multiple organisms interact, each depending on others for survival.
Food webs are more realistic than food chains because they depict the multi-faceted feeding relationships that exist in nature. A single organism can occupy multiple positions in a food web, participating in various feeding pathways. For example, a frog might feed on grasshoppers and other insects, making it an important part of multiple food chains.
The Energetic Pyramid: A Visual Representation of Energy Transfer
The energy pyramid provides a visual representation of energy flow within an ecosystem. It’s shaped like a pyramid, with the producers forming the broad base and the top predators at the apex. Each level represents a trophic level, a feeding level within the food chain or web.
Here’s what the energy pyramid illustrates:
- Energy Loss: As energy flows from one trophic level to the next, a significant amount of energy is lost as heat. This is why the pyramid narrows as it ascends; each level holds less energy than the one below it.
- Limited Levels: The pyramid structure explains why there are limited trophic levels within an ecosystem. It requires a large base of producers to support a small number of top predators.
- Food Web Stability: A diverse food web, with multiple interconnected pathways, promotes stability. If one species is removed, the ecosystem can still function.

Image: printablelibcolor.z13.web.core.windows.net
The Importance of Food Chains, Food Webs, and the Energy Pyramid
These concepts are crucial for understanding the intricate balance of life on Earth. They help us appreciate the connections within ecosystems and the consequences of disrupting these food webs. For example, the introduction of invasive species can disrupt food webs, leading to population declines or even extinctions.
These concepts are also important for conservation efforts. By understanding how energy flows through ecosystems, we can develop sustainable practices that support biodiversity and ensure the long-term health of our planet.
Worksheet Activities
To solidify your understanding of these concepts, try these engaging activities:
- Drawing a food web: Research the food web of a specific ecosystem (like a coral reef, a forest, or a pond) and draw a detailed diagram.
- Creating your own energy pyramid: Imagine a local farm. Create an energy pyramid by identifying the producers, herbivores, and carnivores present.
- Analyzing real-world scenarios: Research a recent news article about an invasive species disrupting an ecosystem. How is the food web being affected?
Food Chains Food Webs And Energy Pyramid Worksheet
Conclusion: A Symphony of Life
Food chains, food webs, and the energy pyramid represent a symphony of life, interconnected and dependent on each other for survival. By understanding these concepts, we gain a profound appreciation for the intricate balance of nature and the importance of protecting the delicate web of life that sustains us all. Explore further, delve into the interconnectedness of life, and become an advocate for the preservation of our planet’s rich biodiversity.






