Imagine a world where engines are as simple as they are powerful. Enter the 2-stroke engine, a marvel of mechanical ingenuity, where fuel-air mixtures are ignited every other stroke of the piston, leaving a trail of exhilarating power and a distinct, unmistakable smell. But what about its more civilized cousin, the 4-stroke engine? Does it offer a significant advantage, and if so, at what cost?
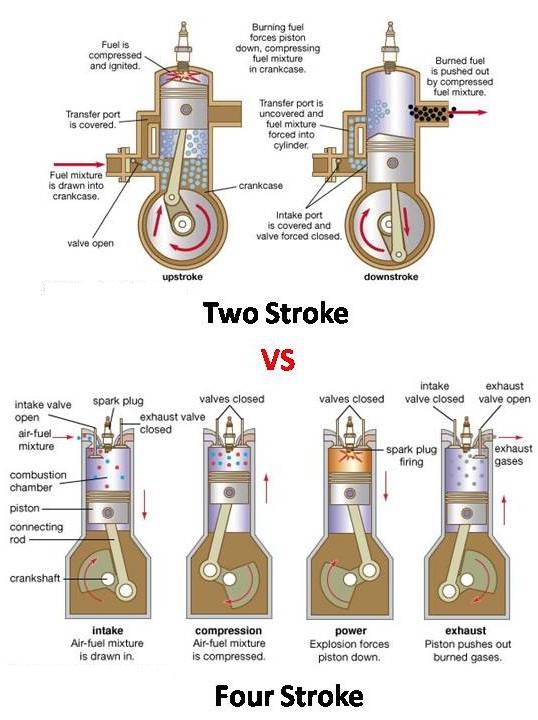
Image: mechanicstips.blogspot.com
The debate between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines has been a long-standing one, each with its own unique strengths and limitations. In this comprehensive guide, we dive into the intricate workings of these two engine types, uncovering their core differences, exploring their applications in various industries, and ultimately, understanding why they continue to hold their respective places in the world of internal combustion.
Understanding the Basics: 2-Stroke vs. 4-Stroke
The 2-Stroke Engine: A Symphony of Simplicity
The 2-stroke engine is a master of efficiency. It operates on the principle of completing its power cycle in two strokes of the piston: the **intake/compression stroke** and the **power/exhaust stroke**. During the intake/compression stroke, a fresh fuel-air mixture is drawn into the crankcase, while the piston moves upwards compressing the mixture. As the piston moves down during the power/exhaust stroke, the compressed mixture is ignited by a spark plug, generating power. The exhaust gases are simultaneously expelled through an exhaust port, often creating the distinctive 2-stroke rumble.
The 4-Stroke Engine: A Refined Powerhouse
The 4-stroke engine takes a more methodical approach, completing its power cycle in four strokes: the **intake stroke**, the **compression stroke**, the **power stroke**, and the **exhaust stroke**. During the intake stroke, air is drawn into the cylinder through an open intake valve. The compression stroke compresses the air, preparing it for combustion. As the piston moves down during the power stroke, the compressed air-fuel mixture is ignited, creating power. Finally, the exhaust stroke expels the spent gases through an exhaust valve.
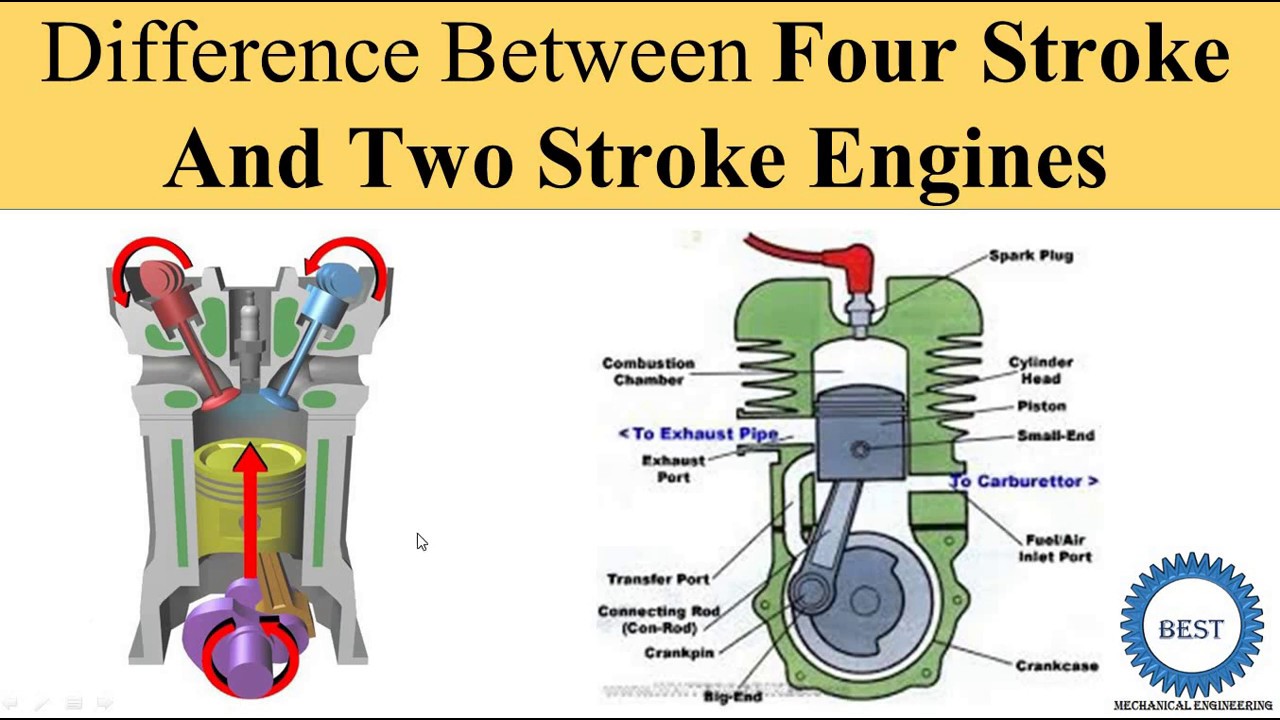
Image: learninglibschuhmancher.z13.web.core.windows.net
Key Differences: A Comparative Analysis
Efficiency: The 2-Stroke Advantage
One stark difference lies in their efficiency. The 2-stroke engine, with its simpler design and quicker power cycle, boasts a higher power-to-weight ratio and often delivers impressive torque, particularly at lower RPMs. This makes it a favorite for applications that demand immediate acceleration and high power output, such as motorcycles, chainsaws, and small boats.
Fuel Consumption: Where the 4-Stroke Shines
However, this efficiency comes at a cost. 2-stroke engines are notorious for their higher fuel consumption, particularly in the older models. This is due to the inherent loss of fuel-air mixture through the exhaust ports, a consequence of its design. The 4-stroke engine, on the other hand, utilizes a more controlled combustion process, resulting in better fuel economy and reduced emissions.
Lubrication: The Separation of Oil and Fuel
Here lies another crucial distinction. The 2-stroke engine relies on **pre-mixing** oil directly with fuel, creating a lubrication system where the oil is burned alongside the fuel. 4-stroke engines, however, employ a **separate lubrication system**, using a designated sump to store oil that is pumped independently to bearings and other friction points. The 4-stroke system minimizes oil consumption and reduces emissions, while the 2-stroke system requires careful oil-to-fuel ratio management and can produce smoky exhaust as a byproduct.
Emissions: The Environmental Battle
The environmental impact of these engines has been a source of significant debate. 2-stroke engines, with their reliance on pre-mixed oil, are known for generating higher emissions. The unburned fuel and oil create a noticeable smoky exhaust and contribute to air pollution. Despite recent advancements in 2-stroke designs, reducing emissions remains a challenge compared to the 4-stroke engine. Modern 4-stroke engines, with their closed-loop combustion systems and sophisticated emissions control technologies, significantly reduce emissions, meeting stringent environmental regulations.
Maintenance: Long-Term Durability vs. Simplicity
While the 2-stroke engine shines in its simplicity, the 4-stroke engine is known for its increased longevity. The separate lubrication system in the 4-stroke engine reduces wear and tear on internal components, contributing to its remarkable durability. 4-stroke engines often undergo extensive maintenance, requiring routine oil changes, valve adjustments, and regular tune-ups. The 2-stroke engine, despite its simplicity, may require more frequent maintenance, particularly concerning the lubrication system and the need for carburetor cleaning.
Applications: Picking the Right Engine for the Job
The choice between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines ultimately boils down to the specific application. The 2-stroke engine, with its compact design, lightweight construction, and high power output, dominates in areas like:
- Motorcycles: Lightweight dirt bikes, motorcycles, and scooters often utilize 2-stroke engines due to their high power-to-weight ratio and compact size.
- Chainsaws and Power Tools: Portable power tools like chainsaws, weed trimmers, and leaf blowers rely on 2-stroke engines for their low weight and immediate power delivery.
- Outboard Motors: Smaller outboard motors for boats, particularly high-performance models, continue to utilize 2-stroke engines for their power and agility.
- Model Engines: Model airplanes, remote-controlled vehicles, and model boats often use 2-stroke engines. Their smaller size and high power output make them perfect for these applications.
The 4-stroke engine, offering greater fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and durability, is favoured in:
- Cars and Trucks: Modern vehicles are powered by 4-stroke engines due to their superior fuel economy, reduced emissions, and compliance with stricter regulations.
- Motorcycles: Larger motorcycles and touring bikes often utilize 4-stroke engines for their smoother operation, improved fuel economy, and quieter performance.
- Industrial Equipment: 4-stroke engines power heavy machinery, generators, and larger industrial equipment due to their reliability, durability, and fuel efficiency.
- Marine Engines: Larger yachts, boats, and marine vessels are typically powered by 4-stroke engines for optimal performance and durability.
The Future of 2-Stroke and 4-Stroke Engines
While the 4-stroke engine has become the dominant power source in many applications, the 2-stroke engine continues to evolve. Advances in technology have led to the development of cleaner and more efficient 2-stroke designs, with direct injection systems, electronic fuel injection, and improved combustion chambers. These advancements have significantly reduced emissions, addressing the environmental concerns associated with traditional 2-stroke engines.
Despite these advancements, the future of the 2-stroke engine likely lies in specialized applications where its inherent advantages remain highly valued. In areas such as small engine manufacturing, power tool industries, and racing, 2-stroke engines are likely to maintain their presence for years to come, providing a balance between power, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Difference Between 2stroke And 4stroke Engine Pdf
Conclusion: A Timeless Debate
The choice between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines is not a simple matter. It is a multifaceted decision influenced by factors such as performance requirements, environmental regulations, maintenance considerations, and cost. While the 4-stroke engine has become the dominant force in many areas, the 2-stroke engine, with its continuous evolution, remains a viable option for specialized applications. Understanding the fundamental differences between these two engine types empowers you to make informed decisions and choose the perfect engine for your specific needs. As we dive deeper into a world of sustainable power solutions, both 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines will continue to play their respective roles, shaping the future of internal combustion technology and driving innovation in the world of mobility and power generation.






