Imagine a world where you could effortlessly predict the properties of any substance just by knowing its position on a chart. This is the power of the periodic table of elements, a visual masterpiece that organizes the fundamental building blocks of our universe. But have you ever wondered about the significance of those seemingly random numbers beneath each element – the atomic masses? While precise atomic masses exist, understanding their rounded counterparts can illuminate fascinating insights into the behavior and reactions of different elements.
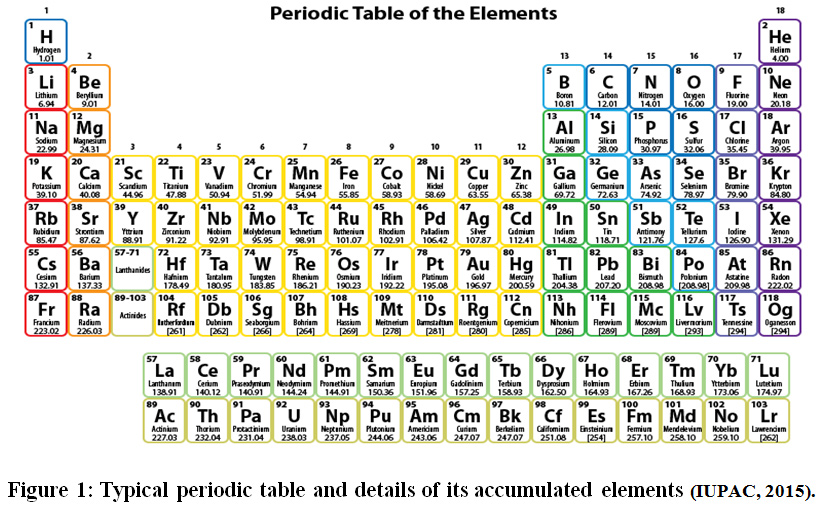
Image: ar.inspiredpencil.com
In this exploration, we’ll embark on a journey into the heart of the periodic table, unraveling the mystery of rounded atomic masses and uncovering their importance in chemistry, physics, and even our everyday lives. This captivating journey will arm you with the knowledge to understand the world around you on a deeper, more fundamental level.
The Dance of Atomic Masses: A Symphony of Protons and Neutrons
At the core of every atom lies its nucleus, a tiny powerhouse containing protons and neutrons. Protons carry a positive charge and determine an element’s identity. Neutrons, on the other hand, are neutral and contribute to the atom’s mass. The atomic mass of an element represents the average weight of all its naturally occurring isotopes, atoms of the same element with varying numbers of neutrons.
For most practical purposes, we often rely on rounded atomic masses. This simplification allows us to quickly grasp the relative weights of different elements, making calculations and predictions easier. For instance, knowing that carbon’s rounded atomic mass is 12 helps us deduce that a carbon atom weighs approximately twelve times more than a hydrogen atom, whose rounded atomic mass is 1.
Navigating the Periodic Table: A Map to Chemical Understanding
The periodic table is a carefully organized arrangement of elements, featuring rows (periods) and columns (groups). Elements within a group share similar chemical properties due to having the same number of valence electrons – those involved in chemical bonding. As we move across a period, the number of protons increases, leading to a gradual increase in atomic mass. This trend is reflected in the rounded atomic masses, which generally increase from left to right.
The periodic table also reveals fascinating insights into the reactivity of elements based on their position. Elements located on the left side of the table are typically metals, characterized by their tendency to lose electrons and form positively charged ions (cations). Conversely, elements found on the right side are mostly nonmetals, readily gaining electrons to form negatively charged ions (anions). Examining the rounded atomic masses of elements within a group can aid in predicting their reactivity and the types of compounds they’re likely to form.
Beyond the Basics: Unveiling the Nuances of Atomic Mass
While rounded atomic masses offer a valuable starting point, the real world of atomic masses is more intricate. The existence of isotopes means that the atomic mass of an element represents an average, rather than a fixed value. Isotopes have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons, resulting in variations in their atomic masses.
For instance, chlorine has two naturally occurring isotopes: chlorine-35 and chlorine-37. Chlorine-35, with 18 neutrons, accounts for approximately 75% of naturally occurring chlorine. Chlorine-37, containing 20 neutrons, makes up the remaining 25%. The atomic mass of chlorine, listed as 35.45, represents the average weight of these two isotopes, weighted by their relative abundance.
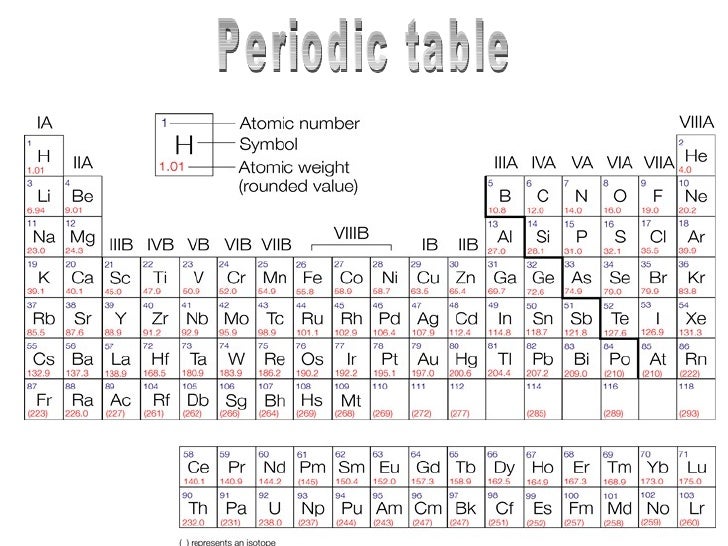
Image: www.slideshare.net
The Importance of Rounded Atomic Masses: Applications in Chemistry and Beyond
Rounded atomic masses play a crucial role in various scientific and practical applications. They serve as a fundamental tool for:
- Stoichiometry: Calculating the amounts of reactants and products in chemical reactions, a cornerstone of chemistry.
- Molecular Weight Calculations: Determining the molecular weight of compounds by adding up the rounded atomic masses of their constituent elements.
- Mass Spectrometry: Identifying unknown compounds by analyzing the masses of their ions, a powerful analytical technique.
- Nuclear Chemistry: Understanding the behavior of isotopes and their role in radioactive decay and nuclear reactions.
Beyond the Science Classroom: Rounded Atomic Masses in Our Everyday Lives
The principles of rounded atomic masses extend beyond the confines of the laboratory and into our daily lives. For example:
- Nutrition: Understanding the role of elements like calcium and iron in our diet, crucial for maintaining good health.
- Materials Science: Designing new materials with specific properties by carefully selecting elements with desired atomic masses.
- Medicine: Developing new drugs and therapies by understanding the interactions of elements at the molecular level.
Expert Insights and Practical Guidance
Dr. Emily Chen, a renowned chemist specializing in periodic table studies, emphasizes the importance of understanding rounded atomic masses: “While precise atomic masses are crucial for certain advanced calculations, rounded atomic masses offer an accessible entry point for comprehending the fundamental principles of chemistry. They allow us to make informed estimations and predict the behavior of elements with relative ease.”
To effectively utilize rounded atomic masses, remember these key points:
- Understand that rounded atomic masses are approximations, not exact values.
- Be aware of the potential for variations, especially when dealing with elements that have multiple isotopes.
- Use rounded atomic masses judiciously, considering the specific context and required level of precision.
Periodic Table Of Elements Rounded Atomic Mass
Embrace the Wonders of the Periodic Table
As we’ve explored the fascinating world of rounded atomic masses, we’ve seen how these seemingly simple numbers unlock a deeper understanding of the elements and their behavior. From the intricate dance of protons and neutrons to the practical applications in science and everyday life, the periodic table stands as a testament to the beauty and complexity of our universe.
So the next time you encounter the periodic table, take a moment to appreciate the significance of those rounded atomic masses. They hold the key to unlocking a world of knowledge and wonder, empowering you to understand the elements that compose everything around us. Embrace the journey, and let the periodic table guide you to a deeper appreciation of the world’s fundamental building blocks.






